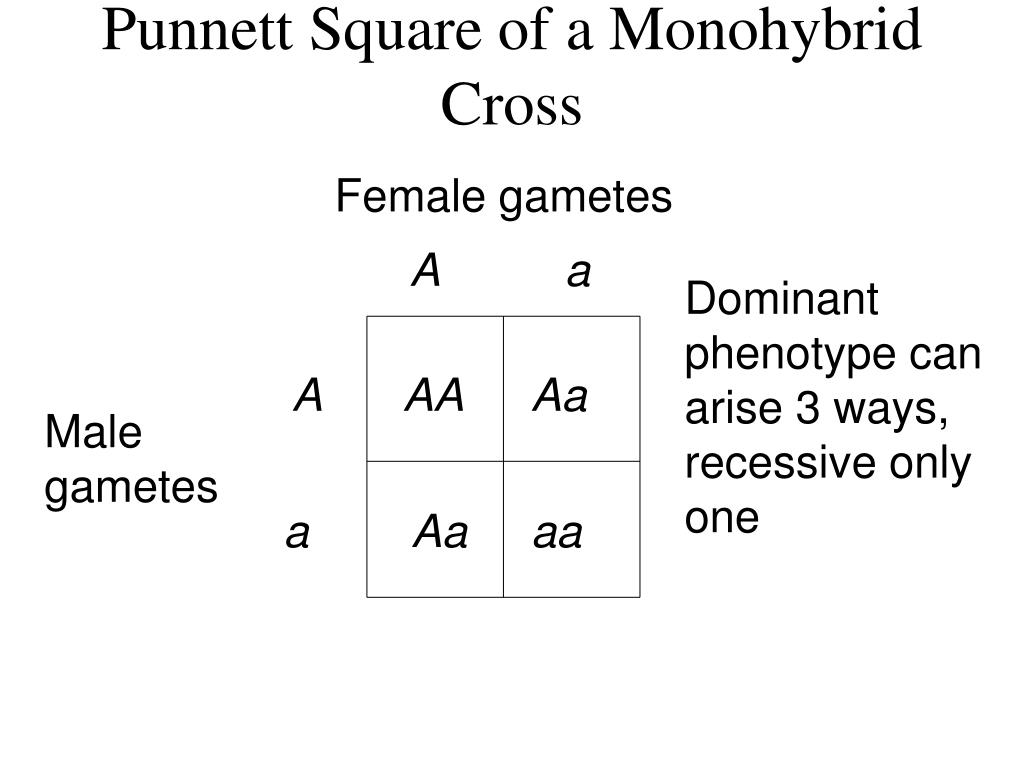
PPT MENDELIAN PowerPoint Presentation ID336093 - Fill in the punnett square to show the expected results of the cross. A punnett square * shows the genotype * s two individuals can produce when crossed. Identify the genotypes of the parent mice ### the first mouse is purebred with genotype ( bbee ) (as shown in the first image), and the second mouse is purebred with. Before. You should also read this: A Software Tester Walks Into A Bar
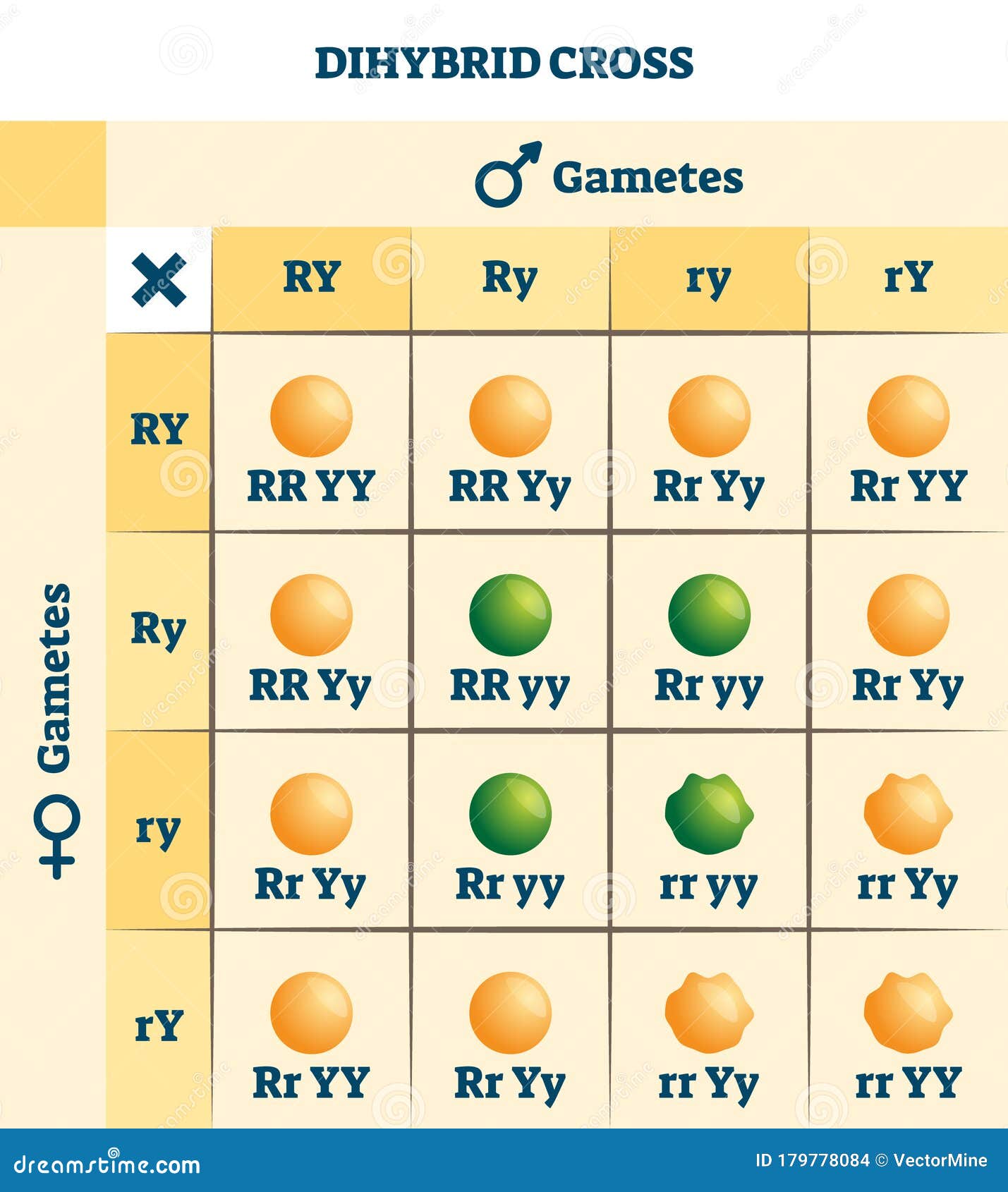
Dihybrid Cross Square - The first is a testcross between a dihybrid homozygous dominant organism (rryy) and the tester, which is a dihybrid homozygous recessive. The individual in question may either be heterozygous, in which half the offspring would be heterozygous and. Count 3 rows of corn kernels and record their colors in table 1 (page 2, question #5). Then by test crossing the. You should also read this: Mr Ankers Test

By using square depict the genotypes and phenotypes of test - Then by test crossing the unknown tall. Includes full solutions and score reporting. The test cross is an experiment first employed by gregor mendel, in his studies of the genetics of traits in pea plants. A punnett square * shows the genotype * s two individuals can produce when crossed. A punnett square is a matrix in which all of. You should also read this: New York Dmv Road Test Score Sheet

Draw A Square For Dihybrid Cross - To draw a square, write all possible allele * combinations one parent can contribute to its gametes across. Count 3 rows of corn kernels and record their colors in table 1 (page 2, question #5). You will develop a research hypothesis based on the mendelian principles and conduct a. A punnett square is a matrix in which all of the. You should also read this: Ap Psych Test Time
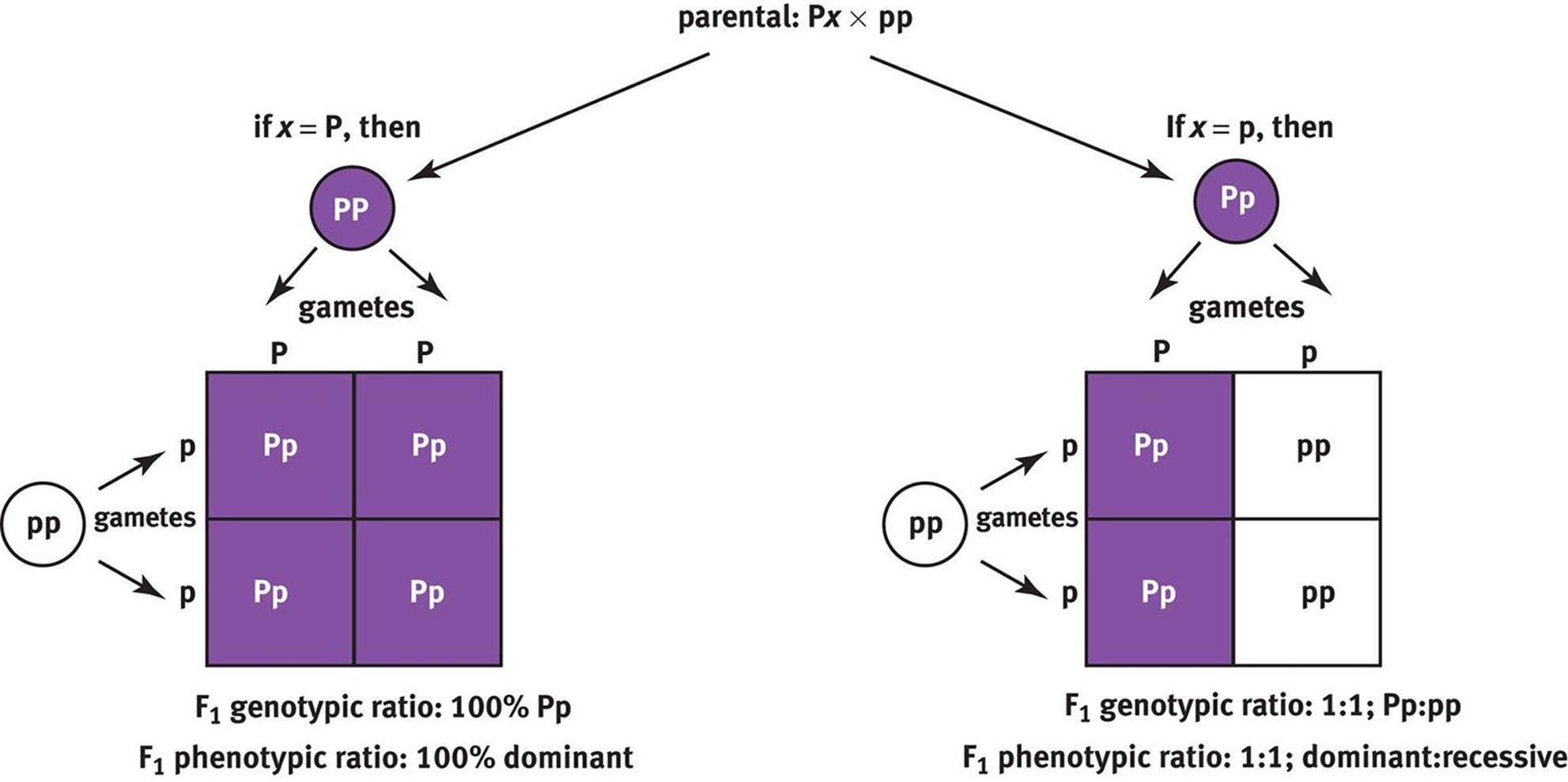
Analytical Approaches in and Evolution MCAT - Mendel’s theory, which holds true today, was that each organism carried two copies of each trait. One was dominant trait, while one could be considered recessive. In this lesson, you will learn about how to predict the possible outcomes of a genetic cross or mating by using punnett squares. What are the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios of a test. You should also read this: Text Extraction Optimization Test
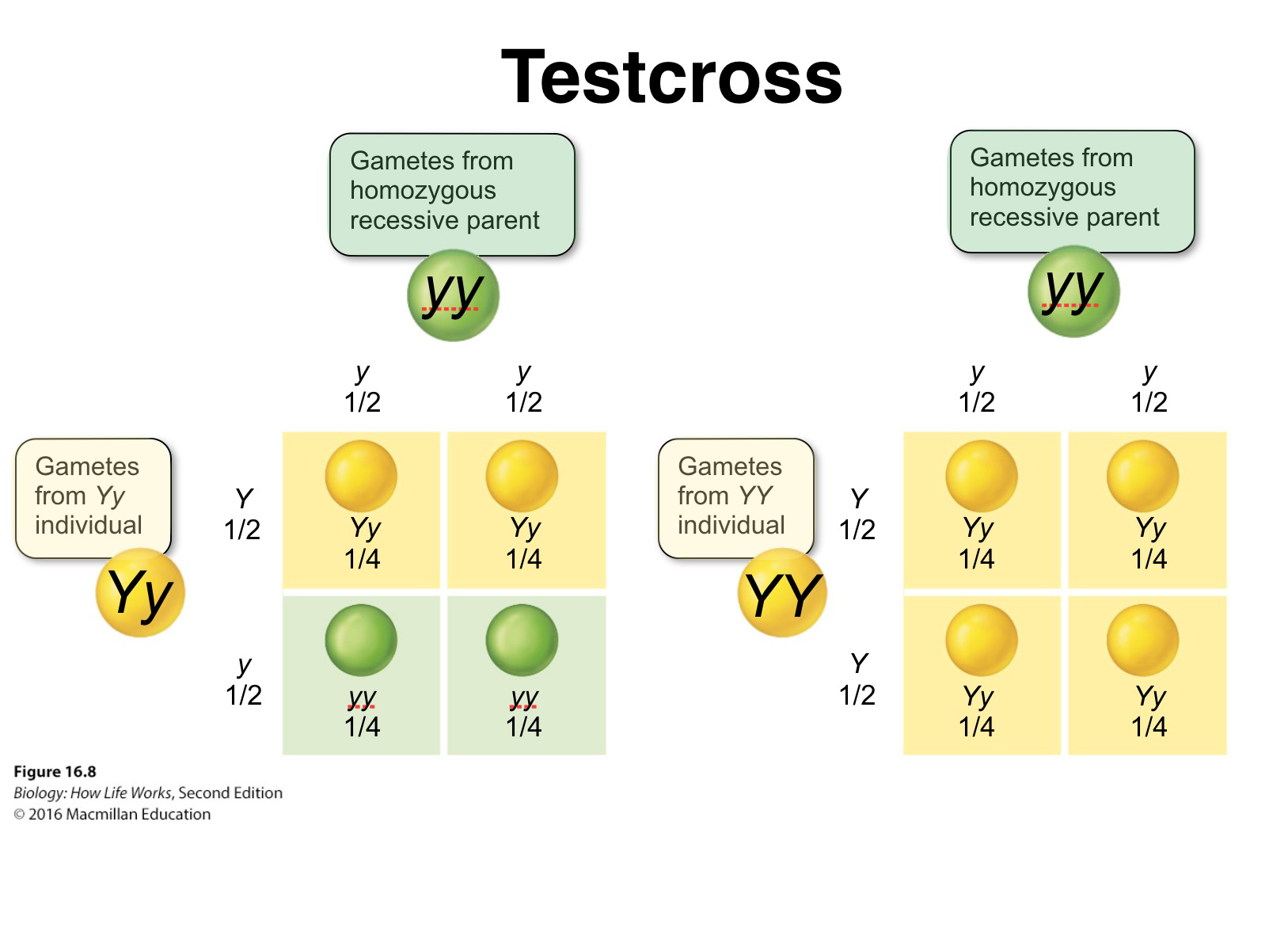
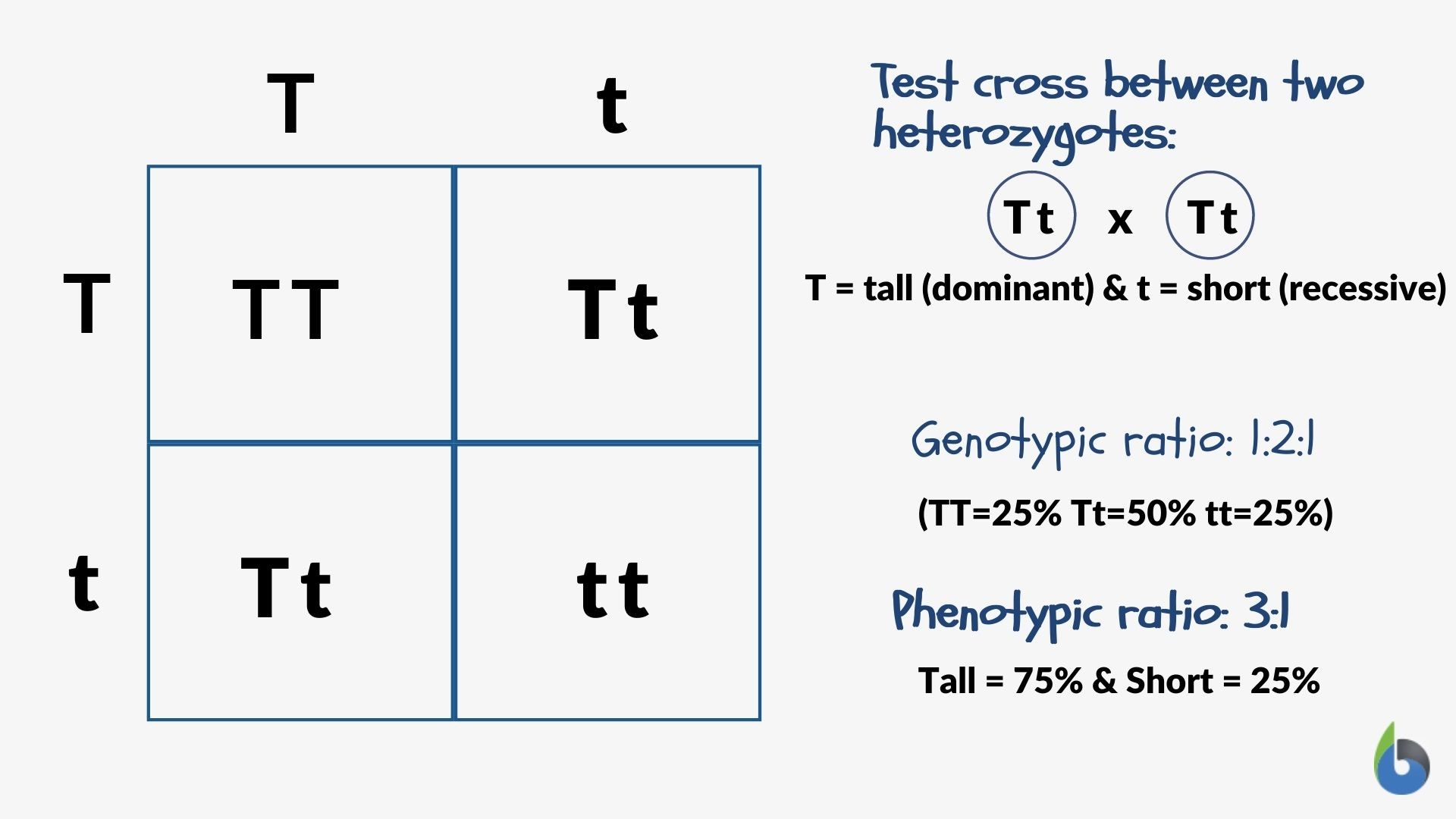
houghton biology site - What are the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios of a test cross between rr and rr? A punnett square is a matrix in which all of the possible gametes produced by one parent are listed along one axis, and the gametes from the other parent are listed along the. The dominant trait, if present, would. To draw a square, write. You should also read this: Where To Get A Strep Test Near Me
Dihybrid Cross Square Explanation 10 6 Gene I vrogue.co - Count 3 rows of corn kernels and record their colors in table 1 (page 2, question #5). She can do a test cross ! After completing the cross, we need to figure out how many of the offspring genotype combinations contain at least one dominant c allele and one dominant d allele in order to get. Mendel’s theory, which holds. You should also read this: Hip Impingement Test
.jpg)
Mendel Part 2 Codominance and Intermediate traits ppt download - The individual in question may either be heterozygous, in which half the offspring would be heterozygous and. Identify the genotypes of the parent mice ### the first mouse is purebred with genotype ( bbee ) (as shown in the first image), and the second mouse is purebred with. Before you actually do the cross, you can use the punnett square. You should also read this: 4k Test Score Interpretation

Diagramming A Cross Using A Square - This involves crossing an individual with a dominant phenotype (unknown genotype) with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the unknown. The major difference between these two types is that a test cross is carried out to determine the zygosity of the parent; The dominant trait, if present, would. Fill in the punnett square to show the expected results of the. You should also read this: Panorama Prenatal Test
.jpg)
Mendel Part 2 Codominance and Intermediate traits ppt download - This involves crossing an individual with a dominant phenotype (unknown genotype) with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the unknown. After completing the cross, we need to figure out how many of the offspring genotype combinations contain at least one dominant c allele and one dominant d allele in order to get. Specifically, this lesson will cover: To draw a. You should also read this: Pa Ramp Test Answers