
Nursing School Info, Nursing School Essential, Nursing Student Tips - Involuntary lifting of the legs upon lifting a patient's head. Nuchal rigidity is elicited by bending the patient's neck forward to touch the chin to the anterior chest. Meningismus is characterized by the signs and symptoms of nuchal rigidity (neck stiffness), photophobia (sensitivity to bright light), and headache. This page includes the following topics and. The examiner flexes the patient’s. You should also read this: How To Study For An English Test

Module 7 Neoplasm and Infections, Cerebral Stroke, Limbic System - Nuchal rigidity is a stiffness that prevents bending of the neck, often caused by meningeal irritation. This page includes the following topics and. Nuchal rigidity was somewhat more useful as an indicator, but it still had limited sensitivity (30 percent). Derived from the nih umls (unified medical language system) updated monthly. Nuchal rigidity is one of the classical signs of. You should also read this: Covert Narcissist Test For Someone Else
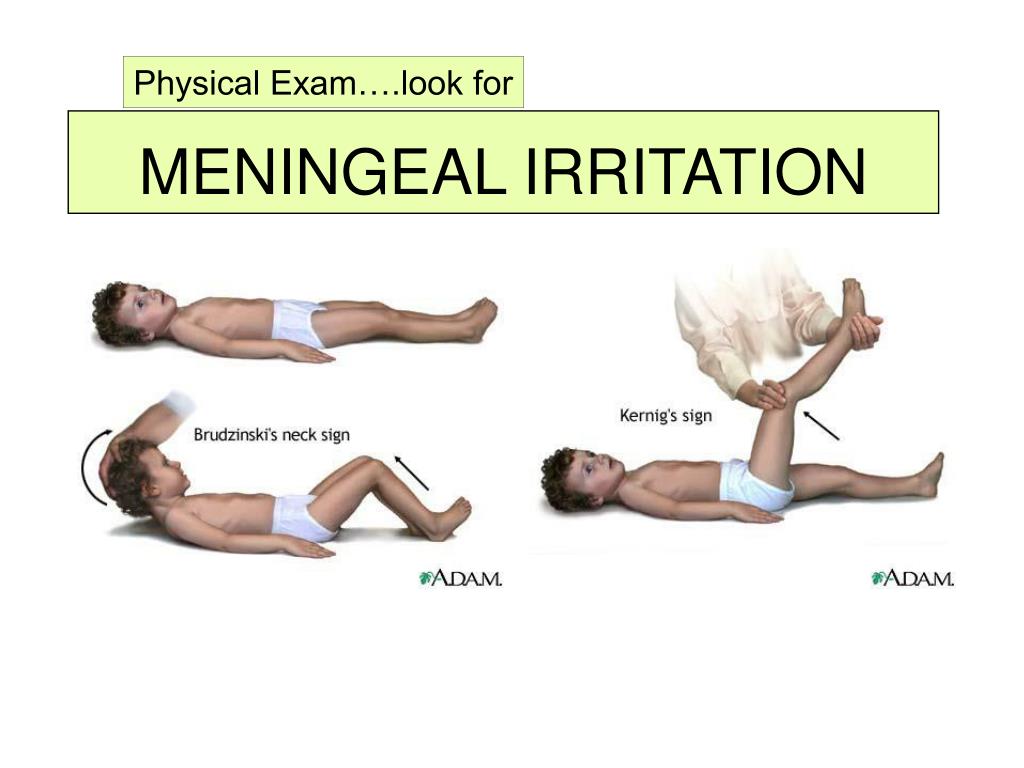
Nuchal Rigidity - Nuchal rigidity is neck stiffness caused by various conditions, such as meningitis, arthritis, or degenerative disk disease. 1 with other meningeal signs such as brudzinski sign and kernig sign,. The examiner flexes the patient’s neck to check for nuchal rigidity; When the neck cannot flex forward all the way, nuchal rigidity (neck stiffness) is present. If there is palpable resistance. You should also read this: Goodrx Freestyle Lite Test Strips
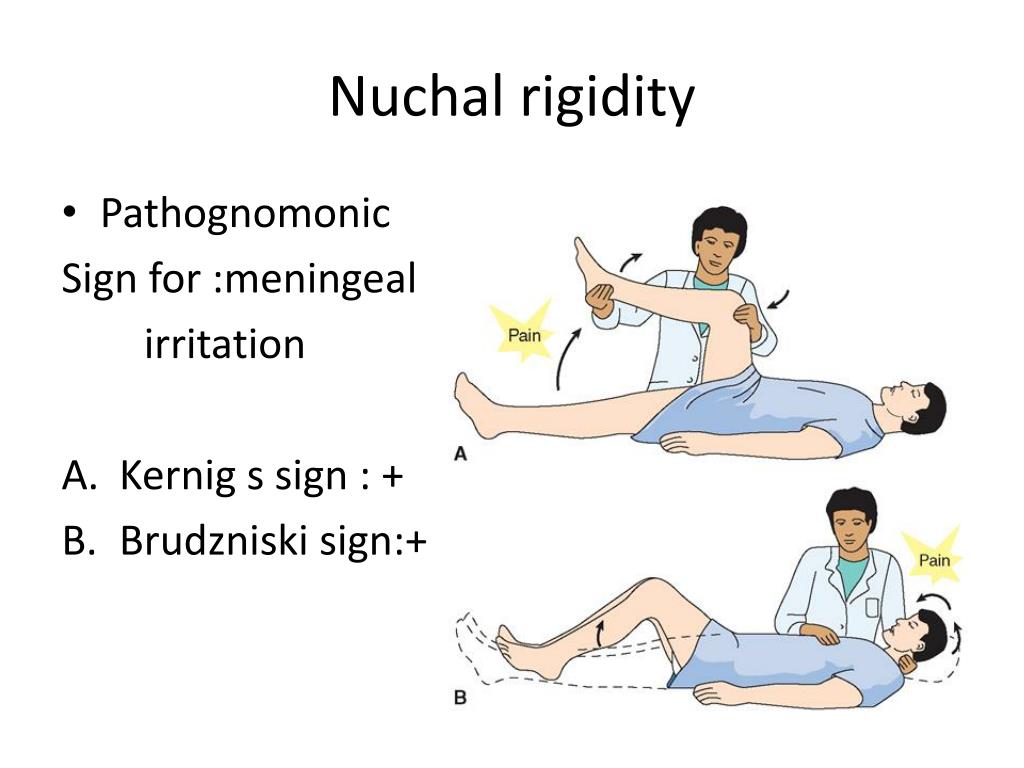
PPT Meningitis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1917228 - Nuchal rigidity is one of the classical signs of meningitis, along with kernig's sign and brudzinski's sign. In this meta‐analysis, we compared the clinical significance and reliability of nuchal rigidity test, jolt accentuation, kernig's sign, and brudzinski's sign in the prediction of csf pleocytosis. The brudzinski sign is a physical maneuver that tests for nuchal rigidity, a symptom of meningitis.. You should also read this: How To Test Pool Alkalinity

Signs of meningitis are nuchal rigidity, positive Kernig's sign and - It involves flexing the neck and observing the reflex flexion of the hips and. Other symptoms include headache, stiff. This additional sensitivity also came at the price of decreased. Learn about the symptoms, causes, test methods, and treatment options for nuchal. Find out how they compare with other. You should also read this: Cdl Temps Test
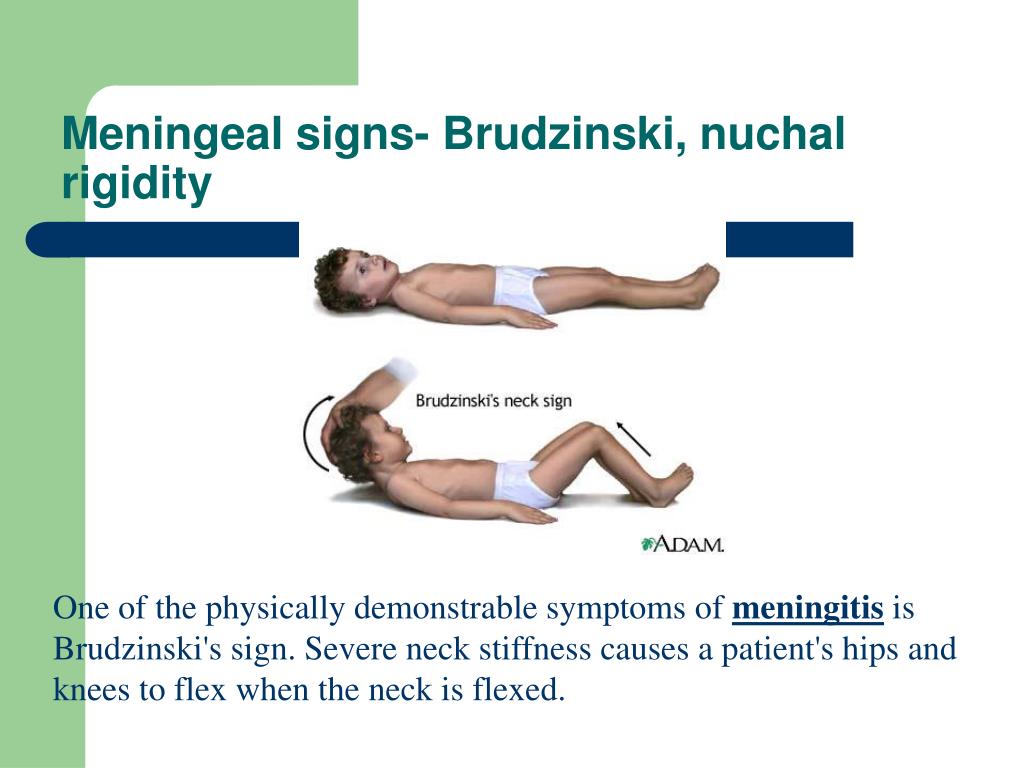
PPT Neurosensory Altered Cerebral Function and Increased - Other symptoms include headache, stiff. Physical exam findings, including nuchal rigidity, kernig, and brudzinski signs, are used at the bedside to help diagnose suspected meningitis cases. Nuchal rigidity is one of the classical signs of meningitis, along with kernig's sign and brudzinski's sign. If there is palpable resistance to passive flexion, the test is positive. This page includes the following. You should also read this: Emissions Testing In Colorado Springs
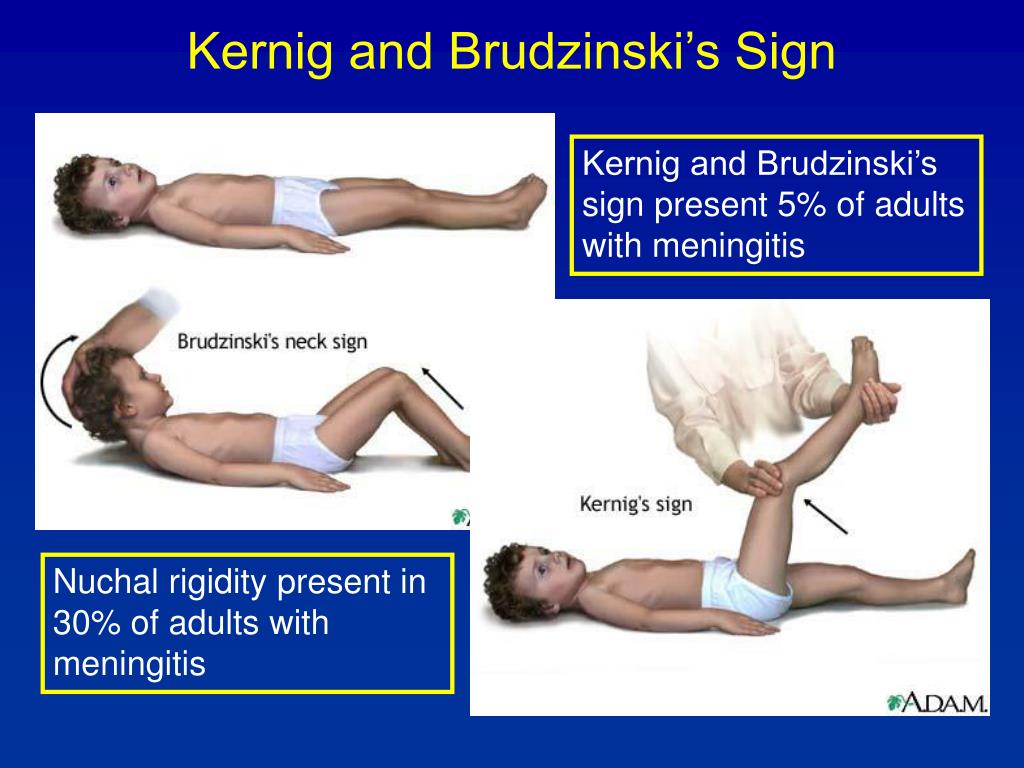
PPT Meningitis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4591726 - The brudzinski sign is a physical maneuver that tests for nuchal rigidity, a symptom of meningitis. Nuchal rigidity is one of the classical signs of meningitis, along with kernig's sign and brudzinski's sign. Nuchal rigidity is a stiffness that prevents bending of the neck, often caused by meningeal irritation. It involves flexing the neck and observing the reflex flexion of. You should also read this: 70 Question Cna Practice Test
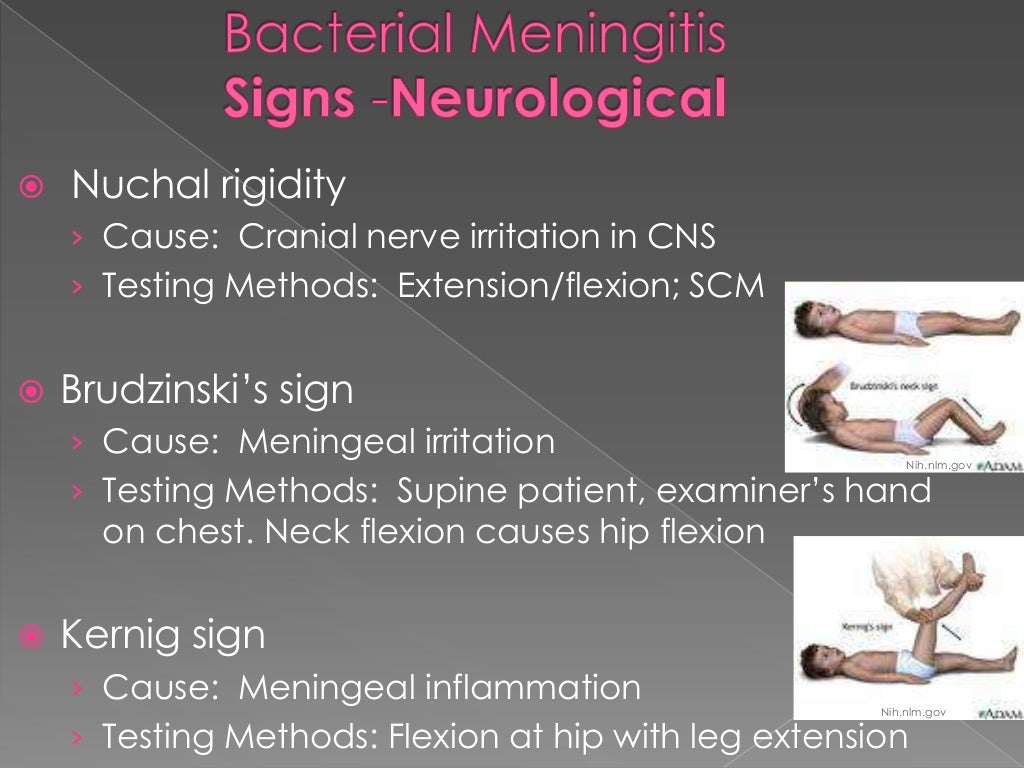
Bacterial meningitis - This could possibly be due to neck muscles stiffening to. Nuchal rigidity was somewhat more useful as an indicator, but it still had limited sensitivity (30 percent). Derived from the nih umls (unified medical language system) updated monthly. While the physical exam, including the assessment of nuchal rigidity, kernig’s sign, and brudzinski’s sign, is crucial for raising suspicion of meningitis,. You should also read this: Drug Test Rite Aid

3 S/S of meningitis nuchal rigidity, positive Kernig, and Brudzinski - 1 with other meningeal signs such as brudzinski sign and kernig sign,. Nuchal rigidity is elicited by bending the patient's neck forward to touch the chin to the anterior chest. Other symptoms include headache, stiff. Nuchal rigidity is one of the classical signs of meningitis, along with kernig's sign and brudzinski's sign. Nuchal rigidity is neck stiffness caused by various. You should also read this: Weber Test Tuning Fork
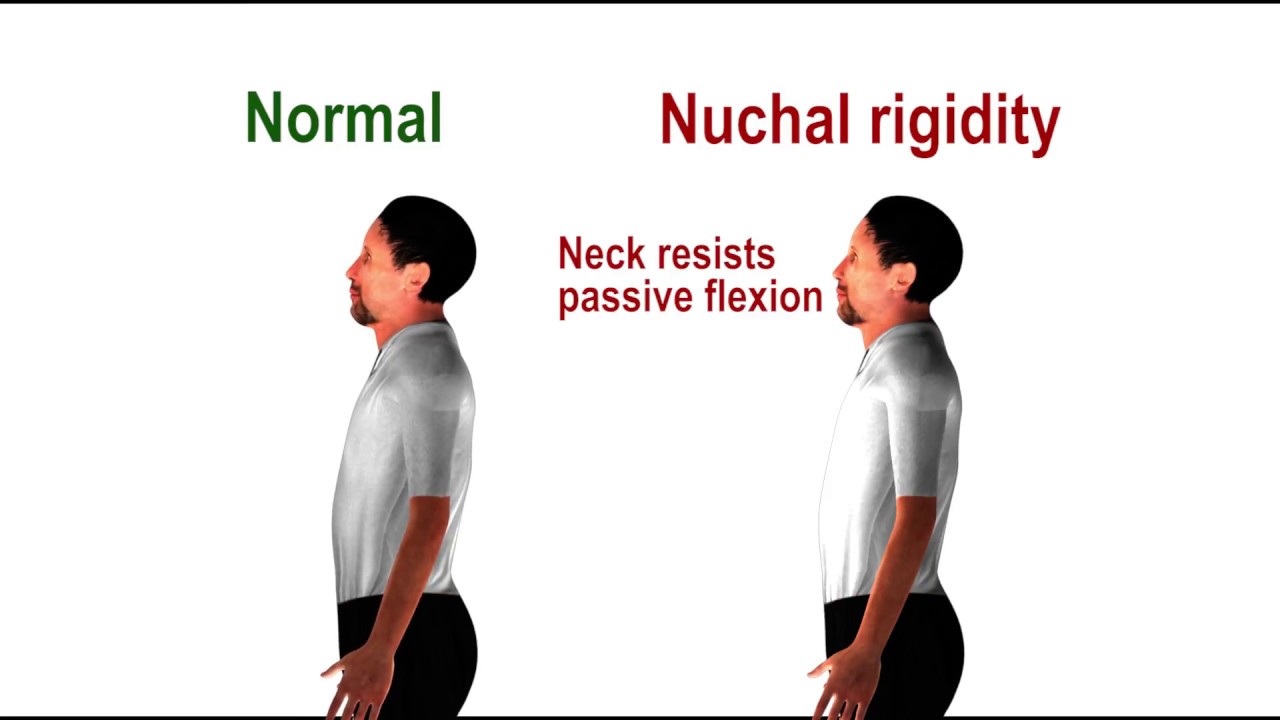
Nuchal rigidity pathognomonic sign of meningeal irritation YouTube - If there is palpable resistance to passive flexion, the test is positive. Learn how to recognize the signs, when to see a. This article reviews the evidence for the diagnostic accuracy of these signs and their. In this meta‐analysis, we compared the clinical significance and reliability of nuchal rigidity test, jolt accentuation, kernig's sign, and brudzinski's sign in the prediction. You should also read this: Hisoka Personality Test