
3 S/S of meningitis nuchal rigidity, positive Kernig, and Brudzinski - Physical exam maneuvers for nuchal rigidity include the kernig and brudzinski signs. Physical exam maneuvers for nuchal rigidity include the kernig’s and brudzinski’s signs. How to perform the nuchal rigidity test. To test for nuchal rigidity, the examiner flexes the patient’s neck and the test is positive if there is palpable resistance to passive flexion. These classical signs are nuchal. You should also read this: Clearblue Negative Test
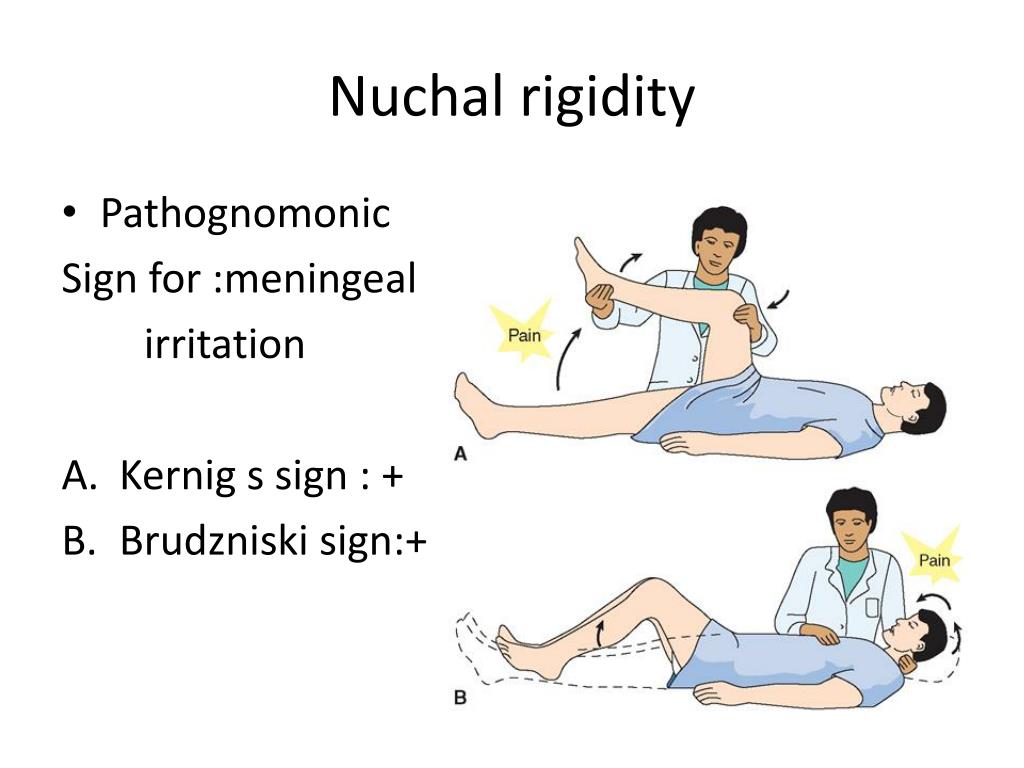
PPT Meningitis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1917228 - How to perform kernig's sign. The classic triad of meningitis symptoms is nuchal rigidity (i.e., neck stiffness), fever, and headache. If you feel pain while gradually extending. The physiological reasons behind these tests. At present, physical examination tests for meningitis mainly comprise the following four maneuvers: You should also read this: Apl Blood Test

Kernig Sign Signs Of Meningitis, Brudzinksi, And Nuchal, 42 OFF - These classical signs are nuchal rigidity, kernig's sign and brudzinski's sign. Physical exam maneuvers for nuchal rigidity include the kernig’s and brudzinski’s signs. If you feel pain while gradually extending. You’ll be asked to lie down with your legs and knees flexed. The classic triad of meningitis symptoms is nuchal rigidity (i.e., neck stiffness), fever, and headache. You should also read this: Prometric Testing Center Greensboro Nc
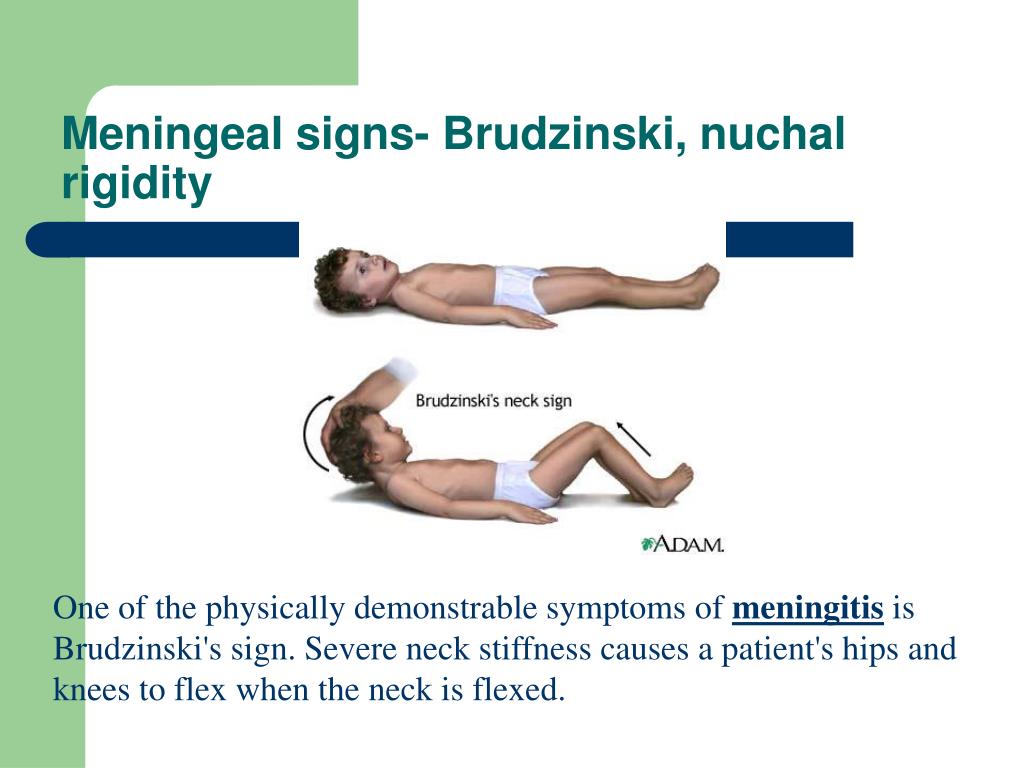
PPT Neurosensory Altered Cerebral Function and Increased - Signs may include nuchal rigidity, kernig’s sign, brudzinski’s sign or jolt accentuation headache. Physical exam maneuvers for nuchal rigidity include the kernig’s and brudzinski’s signs. Each of these relies on the principle that stretching the inflamed meningeal membranes causes clinically detectable. While the physical exam, including the assessment of nuchal rigidity, kernig’s sign, and brudzinski’s sign, is crucial for raising. You should also read this: Idexx Snap 4dx Test
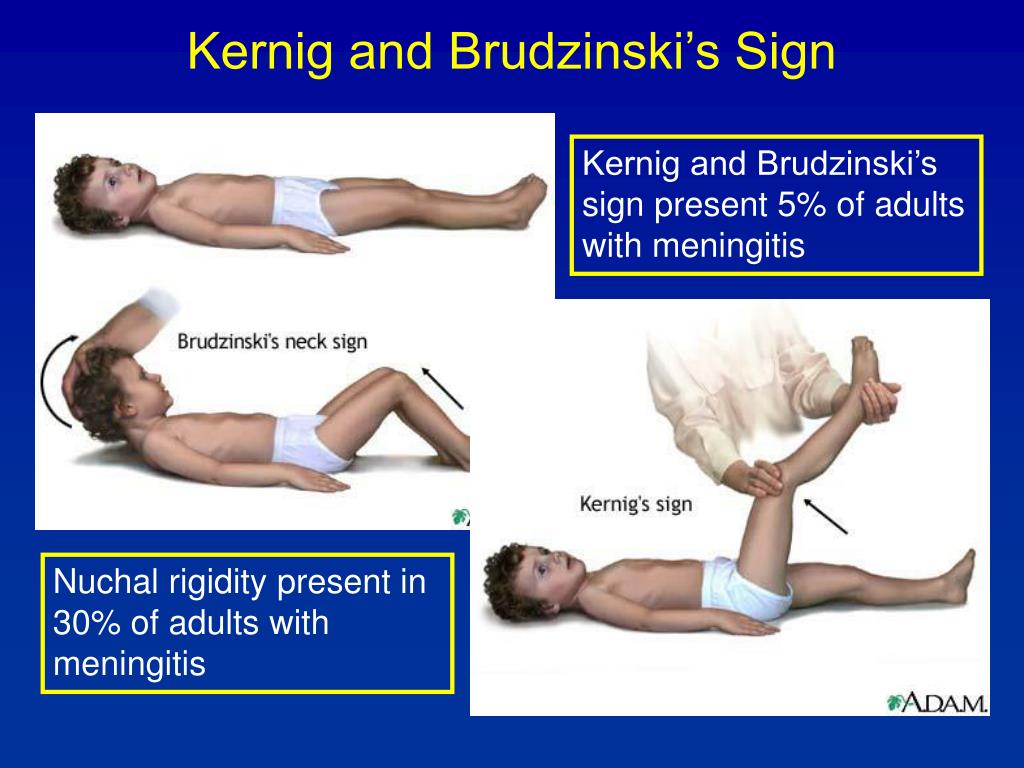
Nuchal Rigidity Meningitis - Kernig's is performed by having the supine patient, with hips and knees flexed, extend. If meningitis is suspected, a lumbar puncture can analyze cerebrospinal. Each of these relies on the principle that stretching the inflamed meningeal membranes causes clinically detectable. Nuchal rigidity (neck stiffness), jolt accentuation, kernig's sign, and brudzinski's. Kernig’s is performed by having the supine patient, with hips. You should also read this: Prometric Hca Skills Test

Module 7 Neoplasm and Infections, Cerebral Stroke, Limbic System - Nuchal rigidity (neck stiffness), jolt accentuation, kernig's sign, and brudzinski's. At present, physical examination tests for meningitis mainly comprise the following four maneuvers: If meningitis is suspected, a lumbar puncture can analyze cerebrospinal. Your doctor may start the diagnosis with a routine checkup and medical history, which will include collecting information related to. How to perform brudzinski's sign. You should also read this: How To Read A Pregnancy Strip Test

Nuchal Rigidity Meningitis - You’ll be asked to lie down with your legs and knees flexed. To diagnose meningitis, many doctors rely on tests such as: The physiological reasons behind these tests. How do you perform nuchal rigidity? Kernig’s is performed by having the supine patient, with hips and knees flexed, extend the leg. You should also read this: Carbohydrate Tolerance Test
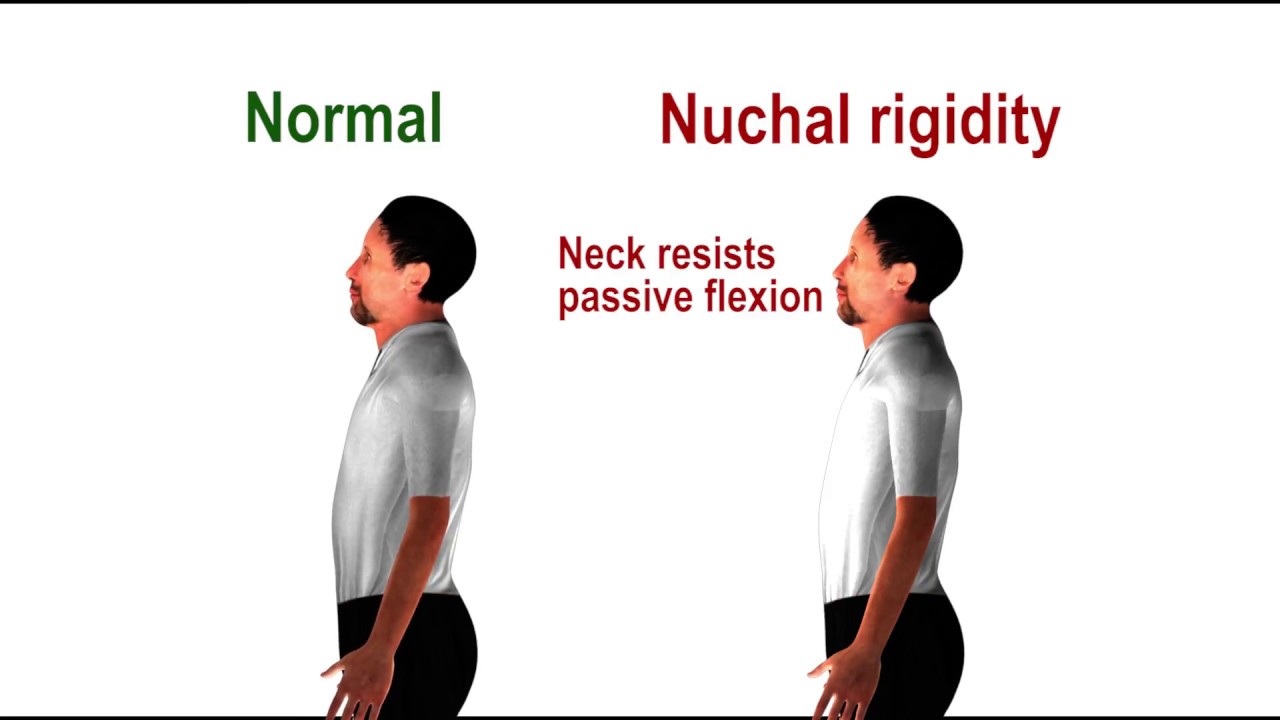
Nuchal rigidity pathognomonic sign of meningeal irritation YouTube - To test for nuchal rigidity, the examiner flexes the patient’s neck and the test is positive if there is palpable resistance to passive flexion. These classical signs are nuchal rigidity, kernig's sign and brudzinski's sign. The physiological reasons behind these tests. Kernig's is performed by having the supine patient, with hips and knees flexed, extend. Definitive diagnosis of meningitis is. You should also read this: Math Placement Test Umd
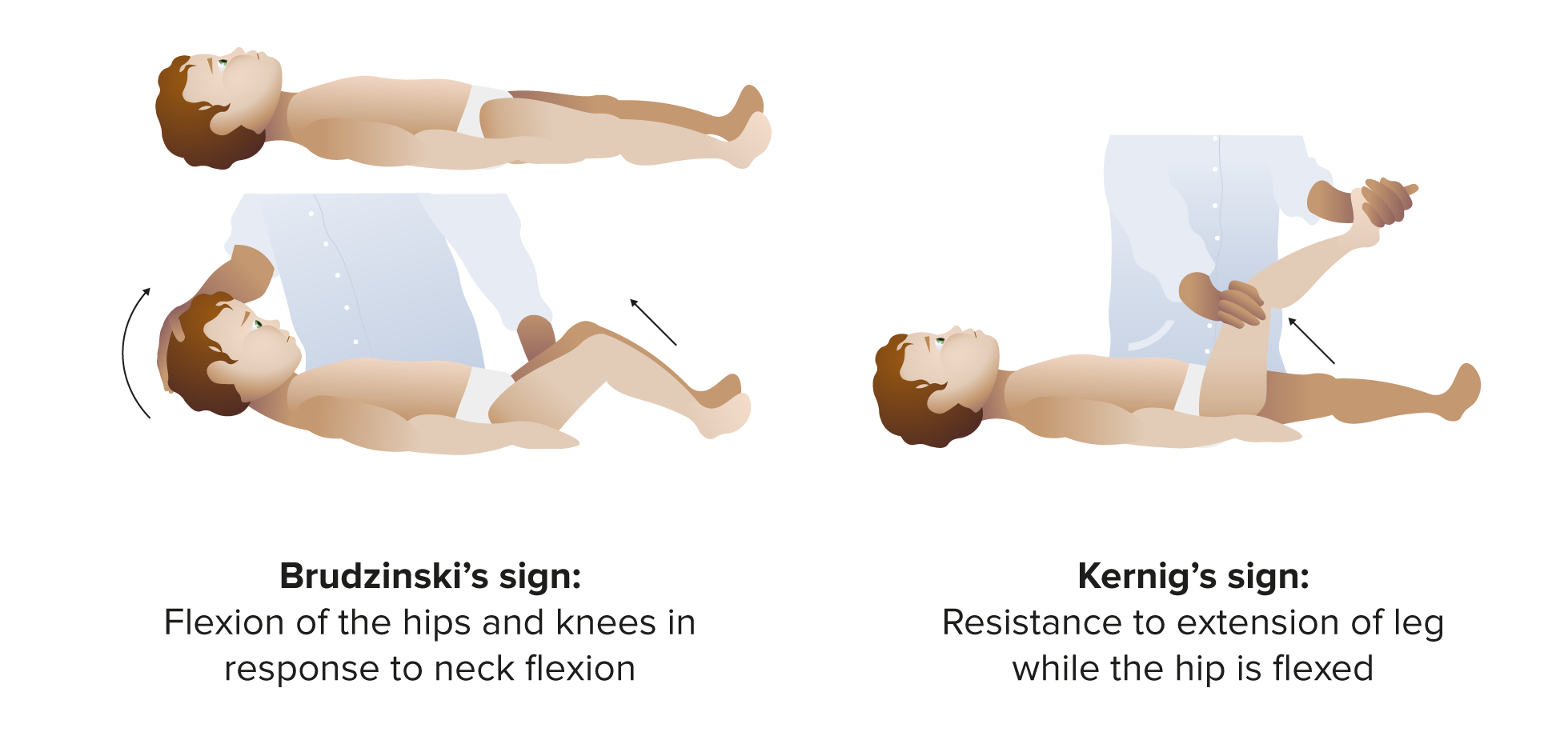
Nuchal Rigidity Meningitis - At present, physical examination tests for meningitis mainly comprise the following four maneuvers: To test for nuchal rigidity, the examiner flexes the patient’s neck and the test is positive if there is palpable resistance to passive flexion. The classic triad of meningitis symptoms is nuchal rigidity (i.e., neck stiffness), fever, and headache. You’ll be asked to lie down with your. You should also read this: Late Period Negative Pregnancy Test White Discharge

Nuchal Area - You’ll be asked to lie down with your legs and knees flexed. How do you perform nuchal rigidity? Nuchal rigidity can be an indicator for meningitis. How to perform kernig's sign. 1 with other meningeal signs such as brudzinski sign and kernig sign,. You should also read this: Squeeze Test High Ankle Sprain