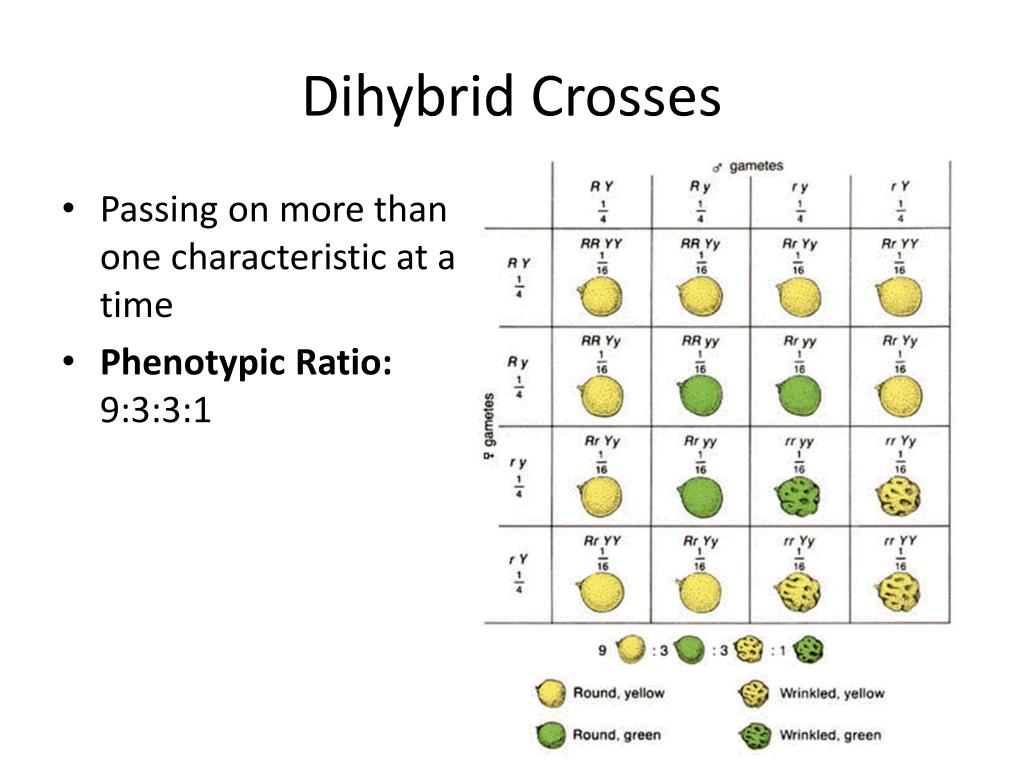
PPT Dihybrid Crosses PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2225652 - The resulting offspring will have a. Typically, a dihybrid cross between two heterozygous individuals results in a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1. A test cross is when you cross a homozygous recessive individual with another individual. In a dihybrid test cross, independent. This method helps researchers and breeders determine whether. You should also read this: Does Casey's Have Pregnancy Tests
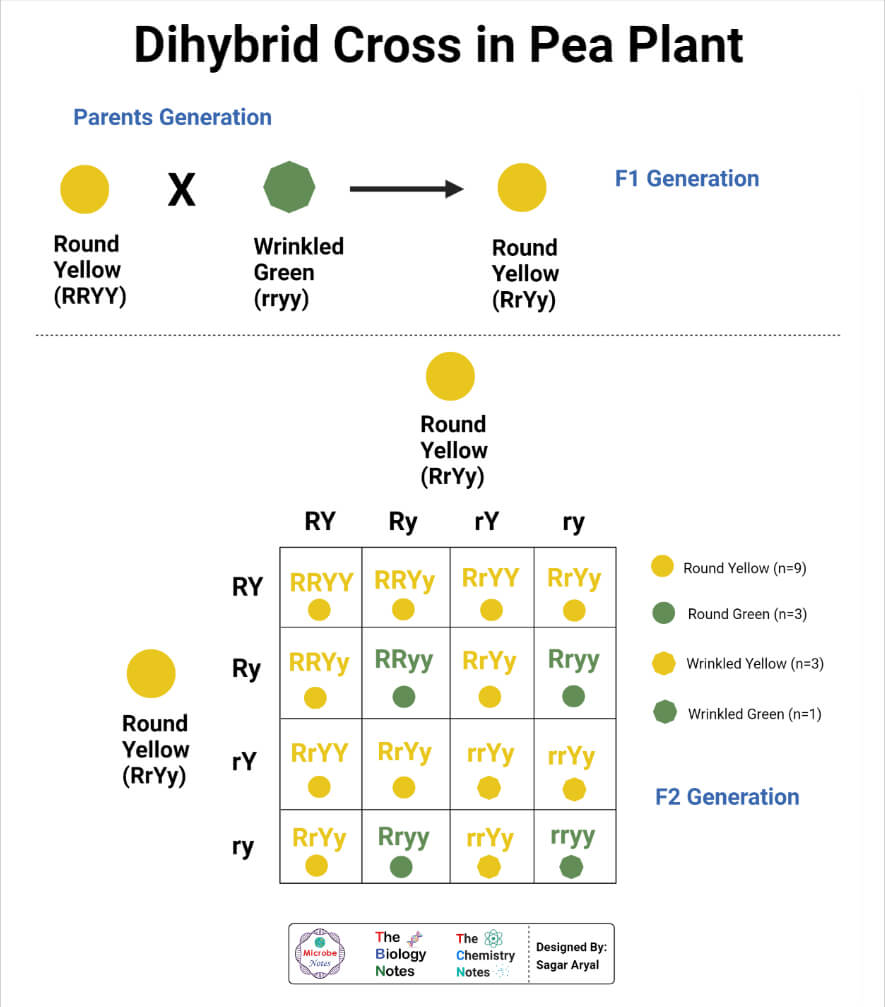
Dihybrid Cross Definition, Steps and Process with Examples - A test cross is when you cross a homozygous recessive individual with another individual. The genotypes of the offsprings are even more diverse with the ratio of. It indicates that two specific genes situated on separate chromosomes. Watch videos, read articles, and complete worksheets to master the. This method helps researchers and breeders determine whether. You should also read this: Kaiser Strep Test

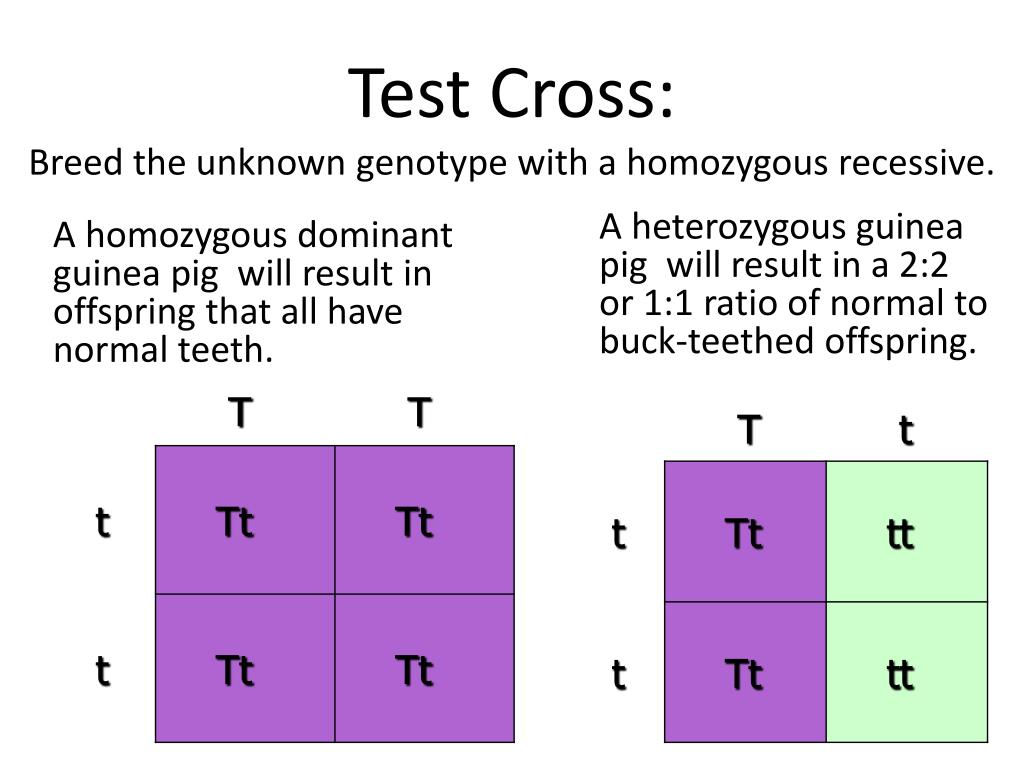
37. A dihybrid test cross ratio for two completely linked genes in a hybr.. - Punnett square for a test cross; The test cross produces four possible genetic combinations rryy, rryy, rryy, and rryy in a ratio of 1:1:1:1. The resulting offspring will have a. A test cross is when you cross a homozygous recessive individual with another individual. Watch videos, read articles, and complete worksheets to master the. You should also read this: Nes Test Prep
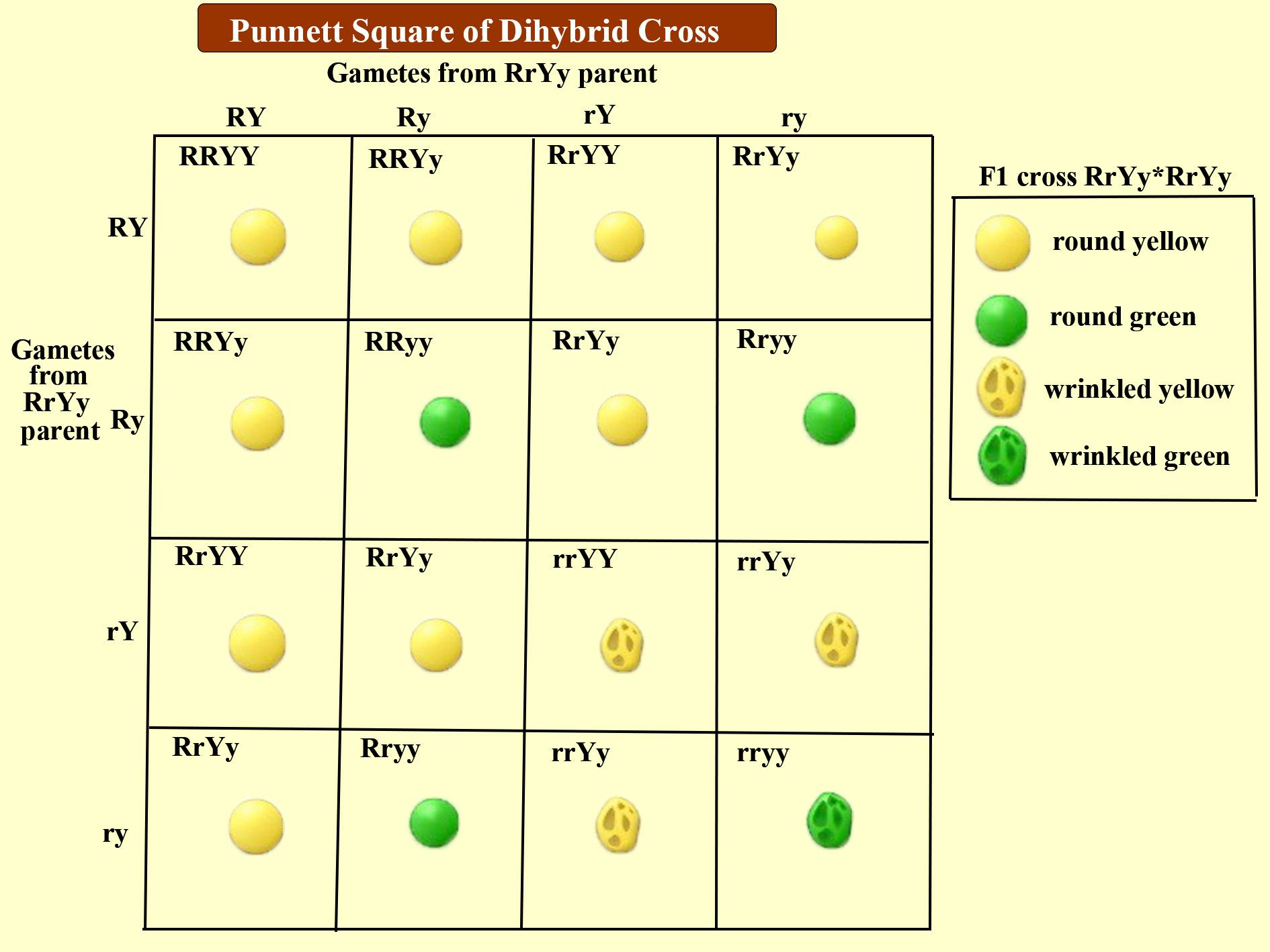
The phenotypic ratio in the dihybrid cross is(a){ 9 }{ 3 }{ 3 }{ 1 - There are two methods to determine the outcome of a dihybrid cross, and the first one is the punnett square, which we will discuss first. In a dihybrid test cross, independent. And min ku kang (eds.),open genetics lectures, fall 2017 (chapter 17, p. While the cross of an f 1 x f 1 gives a ratio of 9:3:3:1, there is. You should also read this: Ap Computer Science Principles Unit 1 Test

THE DIHYBRID CROSS Studying the inheritance of - The genotypes of the offsprings are even more diverse with the ratio of. Watch videos, read articles, and complete worksheets to master the. The test cross produces four possible genetic combinations rryy, rryy, rryy, and rryy in a ratio of 1:1:1:1. Blank punnett squares to fill in the other two possibilities of the test cross [digital images]. In locke, j.,. You should also read this: Nyc State Test Dates

Test Cross Definition and Examples Biology Dictionary - The resulting offspring ratios allow you to determine the genotype of the. This method helps researchers and breeders determine whether. While the cross of an f 1 x f 1 gives a ratio of 9:3:3:1, there is a better, easier cross to test for independent assortment: The genotypic ratio of a. The second method is the branch diagram,. You should also read this: Can You Test Humans For Rabies
PPT Monohybrid & Dihybrid Crosses PowerPoint Presentation, free - While the cross of an f 1 x f 1 gives a ratio of 9:3:3:1, there is a better, easier cross to test for independent assortment: Typically, a dihybrid cross between two heterozygous individuals results in a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1. Understanding the construction of the 9:3:3:1 ratio in dihybrid crosses involves delving into the genetic mechanics that govern the. You should also read this: Toyota Fuel Pressure Test Adapter
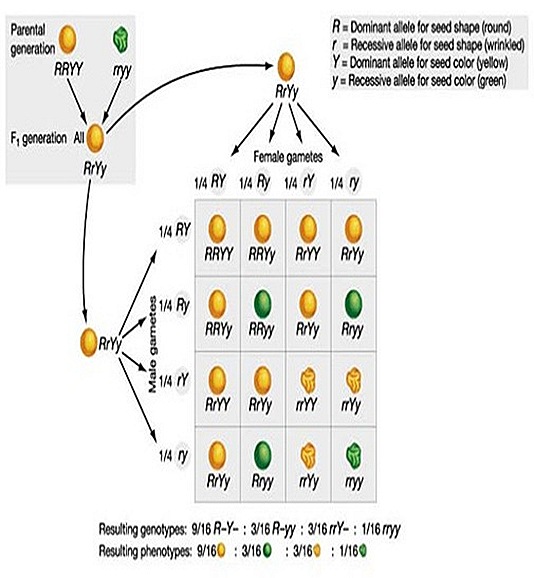
Biology 12 Dihybrid crosses, Mendel's 2nd Law and test crosses - Blank punnett squares to fill in the other two possibilities of the test cross [digital images]. A dihybrid cross is a form of a genetic cross that involves the inheritance of two distinct characteristics. In this case, the 2 allelic pairings are distributed separately into gametes. The genotypic ratio of a. The heterozygous dihybrid individual is known as the tester,. You should also read this: Api Nitrate Test Instructions

What is the Ratio of Dihybrid Cross? - Punnett square for a test cross; Learn the difference between dihybrid cross and dihybrid test cross, and how to apply the ratios for each mating situation. Watch videos, read articles, and complete worksheets to master the. The genotypic ratio of a. The phenotypic ratio of the offsprings in the first generation after a dihybrid cross is written as 9:3:3:1. You should also read this: Test For Subclavian Steal Syndrome
2.1.9.1 Introduction Biology LibreTexts - Learn the difference between dihybrid cross and dihybrid test cross, and how to apply the ratios for each mating situation. In the standard mendel experiment, the phenotypic ratio of the dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1. In locke, j., harrington, m., canham, l. The resulting offspring will have a. In this case, the 2 allelic pairings are distributed separately into gametes. You should also read this: A1 Ase Practice Test