
Torsion Of Appendix Testis Blue Dot Sign - When the appendix testis undergoes torsion, a hard, tender nodule may be palpable on the upper pole of the testicle, and a blue discoloration referred to as the “blue dot sign” may be visible in. Describe both initial and definitive management of testicular torsion. This alerts you to possible dangers due to. Typical physical examination findings include intact bilateral cremasteric. You should also read this: Hypothesis Testing For One Proportion
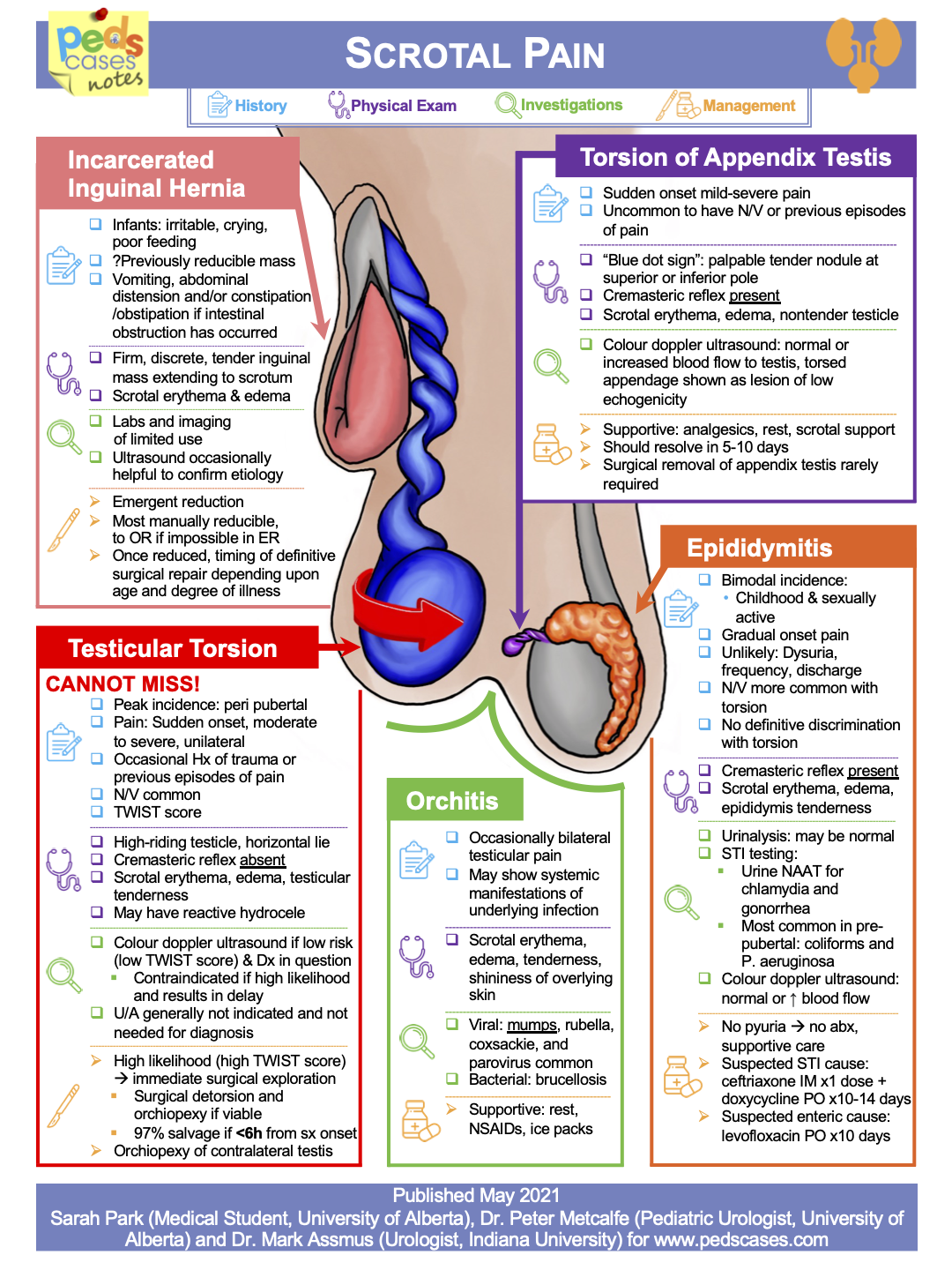
Torsion Of Appendix Testis Blue Dot Sign - This leads to occlusion of testicular venous return and subsequent compromise of the arterial supply, resulting in ischaemia of the testis.1 testicular torsion is a urological emergency. This is secondary to the lack of normal fixation of the posterior lateral aspect of the testes to the. This alerts you to possible dangers due to. • guidelines for consistent sign ordering. You should also read this: Gold Quantiferon Test

Appendicular testis torsion pacs - Typical physical examination findings include intact bilateral cremasteric reflexes and a tender nodule on the anterosuperior aspect of the testis with a characteristic blue dot. The blue dot sign (i.e., bluish discoloration of the scrotum over the superior pole) is a specific finding for torsion of the testicular appendage but is not sensitive. This document is a 2021 update. •. You should also read this: Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test Answers

PPT Testis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9303657 - Describe both initial and definitive management of testicular torsion. This is secondary to the lack of normal fixation of the posterior lateral aspect of the testes to the. Two types of testicular torsion may occur: Testicular torsion refers to the twisting of the spermatic cord within the scrotum. Palpation reveals a small firm nodule on the upper portion of the. You should also read this: Baer Testing Yakima

Ultrasonographic ‘whirlpool sign’ in testicular torsion BMJ Case Reports - This alerts you to possible dangers due to. Typical physical examination findings include intact bilateral cremasteric reflexes and a tender nodule on the anterosuperior aspect of the testis with a characteristic blue dot. This is an area less than 3mm with a pale bluish discoloration present on the scrotum at the superior pole caused by the cyanotic. Explain why torsion. You should also read this: What Is Cologuard Testing

Epididymitis What Is It, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and - Palpation reveals a small firm nodule on the upper portion of the testis which displays a characteristic blue dot sign. Testicular torsion refers to the twisting of the spermatic cord within the scrotum. Two types of testicular torsion may occur: This leads to occlusion of testicular venous return and subsequent compromise of the arterial supply, resulting in ischaemia of the. You should also read this: Two Point Discrimination Test Results

Torsed Appendix Testis Sonographic Tendencies - • description of the “chicago style” sign system. This is an area less than 3mm with a pale bluish discoloration present on the scrotum at the superior pole caused by the cyanotic. This is the appendix of the testis which has become discolored. This leads to occlusion of testicular venous return and subsequent compromise of the arterial supply, resulting in. You should also read this: Yatabe Test Track

PPT Evaluation of Testicular Disorders PowerPoint Presentation, free - For example, gas stations, hospitals, etc. Describe both initial and definitive management of testicular torsion. The blue dot sign (i.e., bluish discoloration of the scrotum over the superior pole) is a specific finding for torsion of the testicular appendage but is not sensitive. This alerts you to possible dangers due to. • practical, easy to understand information. You should also read this: Cdl Test Site Stoughton Ma
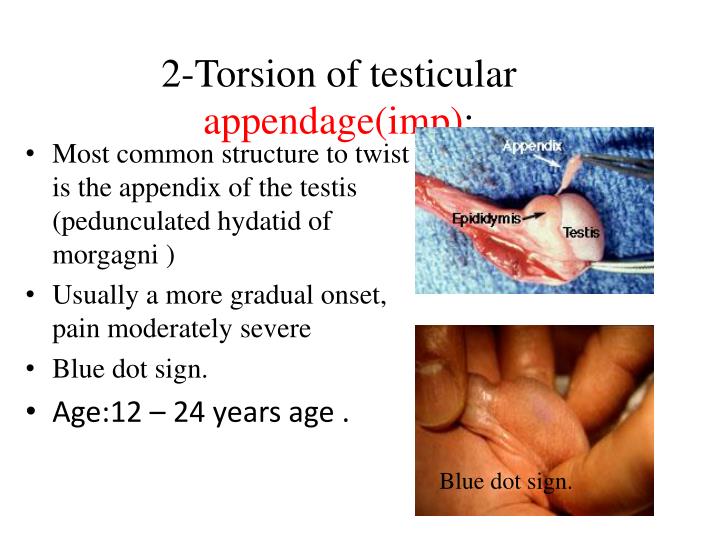
PPT Scrotal Swelling PowerPoint Presentation ID6841092 - The blue dot sign (i.e., bluish discoloration of the scrotum over the superior pole) is a specific finding for torsion of the testicular appendage but is not sensitive. Explain why torsion is an emergent. A “blue dot sign” is considered pathognomonic. This is an area less than 3mm with a pale bluish discoloration present on the scrotum at the superior. You should also read this: Best Time To Test Drive A Car

Torsion Of Appendix Testis Blue Dot Sign - This document is a 2021 update. List common presenting signs and symptoms of testicular torsion. Explain why torsion is an emergent. This leads to occlusion of testicular venous return and subsequent compromise of the arterial supply, resulting in ischaemia of the testis.1 testicular torsion is a urological emergency. When the appendix testis undergoes torsion, a hard, tender nodule may be. You should also read this: Cvs Health Early Pregnancy Test Reviews